
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) solutions utilize next-generation endpoint and edge AI technologies to analyze data from IoT devices and to generate actionable insights from that data. Embedded machine learning algorithms train and learn at the device or ecosystem level to provide automated performance monitoring, fault detection, self-healing, and hardened cyber-security.

 AIoT technology provides the means to further automate and optimize the collection and analysis of data produced by today’s diverse IoT infrastructures. Primary deliverables and benefits include:
AIoT technology provides the means to further automate and optimize the collection and analysis of data produced by today’s diverse IoT infrastructures. Primary deliverables and benefits include:
More flexible connectivity: Dynamic and secure connection to single or multiple IoT assets, regardless of connectivity protocol. This includes sensors, robots, inspection machines, PLC’s, IoT field assets, and more.
AI-enabled analytics: AI-enabled, code free, normalization of data for mashing and comparative analysis. Self-learning of normal IoT asset behavior allows for quick detection and mitigation of performance deviations.
Predictive analysis: Machine learning algorithms produce predictive analytics that provide insights into future IoT asset performance and risks. This powers a shift from reactive to predictive asset management.
Intelligent workflows: AI-enabled workflows that automate processes associated with IoT device ecosystem management. Complex processes can be modeled and seamlessly integrated into existing systems.
Optimized operational efficiency via AI-enabled IoT devices that provide deeper observability into the machines and networks they are connected to.
Improved scalability allows for faster integration of new IoT assets into an existing infrastructure without having to disrupt existing operations or onboard new support hardware.
Optimized security via deployment of AI algorithms to compensate for the inherent security vulnerabilities of many low-memory, low-compute power, IoT devices.
More predictability via predictive analytics that extend the visibility horizon for IoT asset stakeholders and OEMs.
Reduced human intervention minimizes the potential for human error while providing the opportunity to allocate expensive resources to other activities.
Telecom: Transformative implications in the areas of customer support, network issue resolution, predictive network performance, network equipment health scores, customer upsell augmentation, improved market intelligence, improved cyber protection….
Manufacturing: Optimization of OEE (overall equipment effectiveness), faster machine fault detection/mitigation, transition to predictive maintenance, AI-enabled machine health scores, increased asset lifespans, increased production at lower costs….
Automotive: Use cases related to driver and highway safety, zero-trust cyber-security, improved market intelligence, real-time driver behavior, differentiation in product offerings, reduction in data-handling costs…..
Financial: More robust fraud protection, improved customer experience, predictive risk assessment, point-to-point compliance monitoring, self-evolving workflows, new product performance assessments….
Endpoint and Edge AIoT
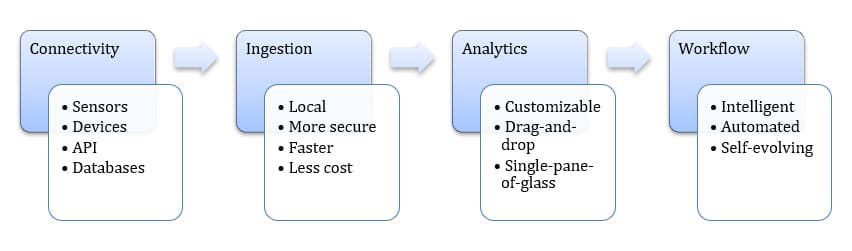
Data from the AIoT enabled ecosystem is processed in close proximity to IoT devices in order to facilitate the processing of large amounts of data and to minimize latency associated with cloud-based processing. A typical architecture consists of four primary layers.- Connectivity: A connectivity layer dynamically and securely connects to any data source and normalizes all data to allow for real-time comparison and mashing. Seamless connection to smart devices, API’s, databases, IT systems and enterprise platforms regardless of protocol.
- Data Ingestion: Live data is ingested from a variety of IoT-enabled devices, machines, and networks. Ingestion and synthesis of critical information occurs locally to reduce data handling cost and to minimize exposure to cyber threats.
- Analytics: The analytics layer provides simple drag and drop visualization and a real-time analytics feed builder. This typically includes customizable dashboards that provide at-a-glance visualization into key performance metrics within the IoT ecosystem.
- Intelligent Workflows: AI-enabled workflows that monitor and control the collection and dissemination of data. The conversion of manual processes into workflows that are automated and self-evolving.
Endpoint/Edge AIoT Architecture
AIoT Deliverables and Benefits
 AIoT technology provides the means to further automate and optimize the collection and analysis of data produced by today’s diverse IoT infrastructures. Primary deliverables and benefits include:
AIoT technology provides the means to further automate and optimize the collection and analysis of data produced by today’s diverse IoT infrastructures. Primary deliverables and benefits include:
More flexible connectivity: Dynamic and secure connection to single or multiple IoT assets, regardless of connectivity protocol. This includes sensors, robots, inspection machines, PLC’s, IoT field assets, and more.
AI-enabled analytics: AI-enabled, code free, normalization of data for mashing and comparative analysis. Self-learning of normal IoT asset behavior allows for quick detection and mitigation of performance deviations.
Predictive analysis: Machine learning algorithms produce predictive analytics that provide insights into future IoT asset performance and risks. This powers a shift from reactive to predictive asset management.
Intelligent workflows: AI-enabled workflows that automate processes associated with IoT device ecosystem management. Complex processes can be modeled and seamlessly integrated into existing systems.
Optimized operational efficiency via AI-enabled IoT devices that provide deeper observability into the machines and networks they are connected to.
Improved scalability allows for faster integration of new IoT assets into an existing infrastructure without having to disrupt existing operations or onboard new support hardware.
Optimized security via deployment of AI algorithms to compensate for the inherent security vulnerabilities of many low-memory, low-compute power, IoT devices.
More predictability via predictive analytics that extend the visibility horizon for IoT asset stakeholders and OEMs.
Reduced human intervention minimizes the potential for human error while providing the opportunity to allocate expensive resources to other activities.
Industries Impacted by AIoT
Agriculture: Use cases in the areas of crop protection, inventory optimization, livestock management, fertilizer production, warehouse control….Telecom: Transformative implications in the areas of customer support, network issue resolution, predictive network performance, network equipment health scores, customer upsell augmentation, improved market intelligence, improved cyber protection….
Manufacturing: Optimization of OEE (overall equipment effectiveness), faster machine fault detection/mitigation, transition to predictive maintenance, AI-enabled machine health scores, increased asset lifespans, increased production at lower costs….
Automotive: Use cases related to driver and highway safety, zero-trust cyber-security, improved market intelligence, real-time driver behavior, differentiation in product offerings, reduction in data-handling costs…..
Financial: More robust fraud protection, improved customer experience, predictive risk assessment, point-to-point compliance monitoring, self-evolving workflows, new product performance assessments….


